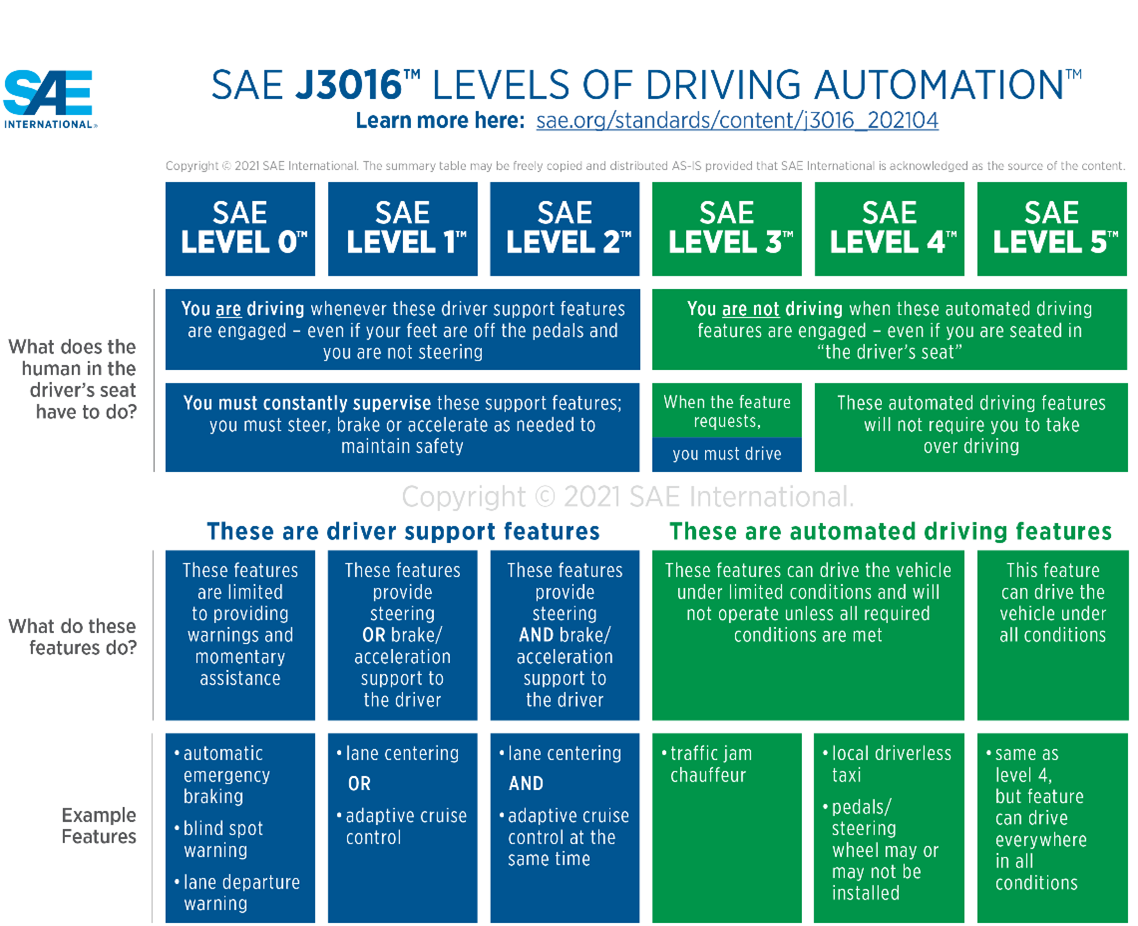
Law of Motion Terminology and Acronym Cheat Sheet
As with many niche areas, mobility has its own “industry speak,” with unique jargon and a multitude of acronyms. Even we sometimes need a cheat sheet to keep everything straight. This is our evolving list.
Government/Regulatory/Industry
AAA: American Automobile Association
Well known “motor club” association that also advocates for safety and other policy goals, including through its Foundation for Traffic Safety.
AUVSI: Association for Uncrewed Vehicle Systems International
International association “dedicated to the advancement of uncrewed systems and robotics.”
IIHS/HLDI: Insurance Institute of Highway Safety/Highway Loss Data Institute
IIHS: Independent, nonprofit scientific and educational organization dedicated to reducing the losses from motor vehicle crashes.
HLDI: A non-profit research organization that publishes scientific studies of insurance data representing the human and economic losses resulting from the ownership and operation of different types of vehicles; publishing insurance loss results by vehicle make and model.
NHTSA: National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
Agency of the DOT charged with promoting transportation safety.
NTSB: National Transportation Safety Board
Independent federal agency responsible for determining the probable cause of transportation accidents and promoting transportation safety.
PAVE: Partners for Automated Vehicle Education
Public education interest group.
SAE: Society of Automotive Engineers
Standard setting organization.
Autonomous and Automated Terminology
AV: Autonomous Vehicle
AVAS: Acoustic Vehicle Alerting Systems
ADS: Automated Driving System
ADAS: Advanced Driver Assistance System
ACC: Adaptive Cruise Control
AEB: Autonomous/Automatic Emergency Braking
BSW: Blind Sport Warning
CIB: Crash Imminent Braking (part of AEB)
DBS: Dynamic Brake Support (part of AEB)
DDT: Dynamic Driving Task
DSSAD: Data Storage for Automated Driving
EDR: Event Data Recorder
Check out Part 1, Part 2, and Part 3 of our EDR Blog Series to learn more.
EV: Electric Vehicle
FCW: Forward Collision Warning
LDW: Lane Departure Warning
ODD: Operating Design Domain
When and under what conditions a vehicle can safely operate.
OEDR: Object and Event Detection and Response
What a vehicle can detect and respond to.
PWS: Pedestrian Warning Systems
RCTA: Rear Cross-Traffic Assist
SDV: Software Defined Vehicles
TSR: Traffic-Sign Recognition
VPD: Vehicle Performance Data
V2I: Vehicle-to-Infrastructure
V2X: Vehicle-to-Everything
V2V: Vehicle-to-Vehicle
V2P: Vehicle-to-Pedestrian
V2C: Vehicle-to-Cloud
Data Laws
CCPA: California Consumer Privacy Act of 2018
CPA: Colorado Privacy Act of 2021
Connecticut Data Privacy Act: Connecticut Act Concerning Personal Data Privacy and Online Monitoring of 2022
CRPA: California Privacy Rights Act of 2020
GDPR: General Data Protection Regulation (EU)
UCPA: Utah Consumer Privacy Act of 2022
VCDPA: Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act of 2021
ADAS DEFINITIONS*
*These definitions are taken from a joint publication by AAA, Consumer Reports, National Safety Council, J.D. Power, and SAE International
Collision Warning and Intervention
Blind Spot Warning: Detects vehicles in the blind spot while driving and notifies the driver to their presence. Some systems provide an additional warning if the driver activates the turn signal.
Forward Collision Warning: Detects a potential collision with a vehicle ahead and alerts the driver. Some systems also provide alerts for pedestrians or other objects.
Lane Departure Warning: Monitors vehicle’s position within the driving lane and alerts driver as the vehicle approaches or crosses lane markers.
Parking Collision Warning: Detects objects close to the vehicle during parking maneuvers and notifies the driver.
Rear Cross Traffic Warning: Detects vehicles approaching from the side at the rear of the vehicle while in reverse gear and alerts the driver. Some systems also warn for pedestrians or other objects.
Automatic Emergency Braking: Detects potential collisions with a vehicle ahead, provides forward collision warning, and automatically brakes to avoid a collision or lessen the severity of impact. Some systems also detect pedestrians or other objects.
Automatic Emergency Steering: Detects potential collisions with a vehicle ahead and automatically steers to avoid or lessen the severity of impact. Some systems also detect pedestrians or other objects.
Reverse Automatic Emergency Braking: Detects potential collisions while in reverse gear and automatically brakes to avoid or lessen the severity of impact. Some systems also detect pedestrians or other objects.
Driving Control and Parking Assistance
Adaptive Cruise Control: Cruise control that also assists with acceleration and/or braking to maintain a driver-selected gap to the vehicle in front. Some systems can come to a stop and continue while others cannot.
Lane Keeping Assistance: Provides steering support to assist the driver in preventing the vehicle from departing the lane. Some systems also assist to keep the vehicle centered within the lane.
Active Driving Assistance: Provides steering and brake/acceleration support to the driver at the same time. The driver must constantly supervise this support feature and maintain responsibility for driving.
Backup Camera: Displays the area behind the vehicle when in reverse gear.
Surround View Camera: Displays the immediate surroundings of some or all sides of the vehicle while stopped or during low-speed maneuvers.
Active Parking Assistance: Assists with steering and potentially other functions during parking maneuvers. Driver may be required to accelerate, brake, and/or select gear position. Some systems are capable of parallel and/or perpendicular parking. The driver must constantly supervise this support feature and maintain responsibility for parking.
Remote Parking Assistance: Without the driver being physically present inside the vehicle, provides steering, braking, accelerating and/or gear selection while moving a vehicle into or out of a parking space. The driver must constantly supervise this support feature and maintain responsibility for parking.
Trailer Assistance: Assists the driver with visual guidance while backing towards a trailer or during backing maneuvers with a trailer attached. Some systems may provide additional images while driving or backing with a trailer. Some systems may provide steering assistance during backing maneuvers.
Other Driver Assistance Systems
Automatic High Beams: Switches between high and low beam headlamps automatically based on lighting and traffic.
Driver Monitoring: Observes driver actions to estimate if they are not engaged in the task of driving. Some systems may monitor eye movement and/or head position.
Heads-Up Display: Projects information relevant to driving into the driver’s forward line of sight.
Night Vision: Improves forward visibility at night by projecting enhanced images on instrument cluster or head-up display.
(last updated September 27, 2022)
Copyright Nelson Niehaus LLC
The opinions expressed in this blog are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the Firm, its clients, or any of its or their respective affiliates. This blog post is for general information purposes and is not intended to be and should not be taken as legal advice.